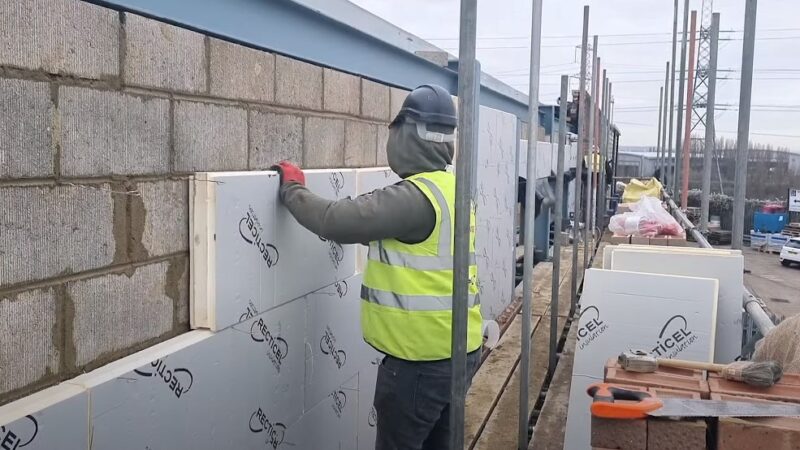
Key Benefits

- Energy Efficiency: Reduces the need for heating and cooling, leading to lower energy bills.
- Comfort: Helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature.
- Environmental Impact: Lower energy consumption means a reduced carbon footprint.
Selecting the Right Insulation Material
The choice of material is pivotal in achieving the desired thermal performance. Two popular types of materials are rigid foam insulation and mineral wool.
Rigid Foam Insulation
- Ideal for achieving a U-value of 0.18W/m² with a thickness of 100mm in masonry walls.
- Highly effective in timber-frame walls, where a thickness of 140mm is recommended.
Mineral Wool
- Requires a thicker layer (170mm) to achieve the same U-value as rigid foam.
- Often preferred for its soundproofing qualities and fire resistance.
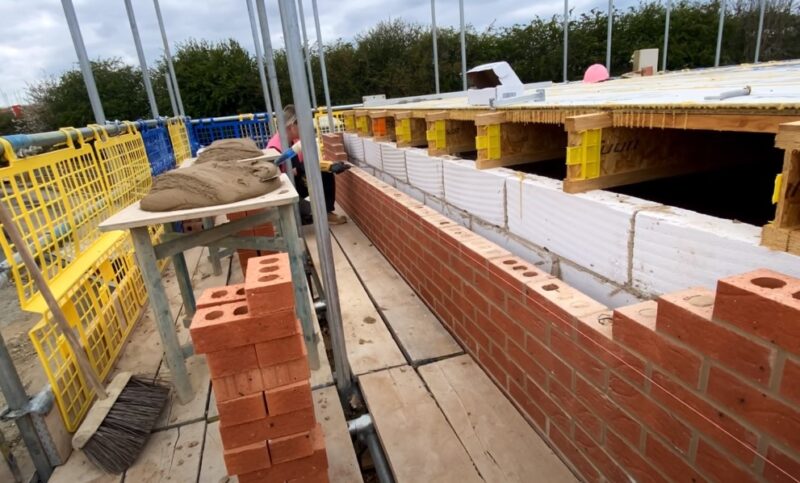
Installation Techniques and Considerations
The installation process varies depending on the type of wall and the chosen insulation material.
Masonry Walls
For masonry walls, proper installation involves careful preparation and attention to detail. The walls must be free of mortar droppings, and the insulation boards should be fitted without leaving any gaps. This process ensures that the insulation performs optimally, reducing the risk of thermal bridges and energy loss.
Timber-Frame Walls
In timber-frame walls, the focus should be on achieving a snug fit for the insulation material. This is crucial to prevent thermal bridges, which are areas where heat can escape more easily, undermining the insulation’s effectiveness.
Comparison of Cavity Wall Insulation Costs, Energy Savings, and Carbon Dioxide Reductions
House Type
Installation Cost (£)
Annual Energy Bill Savings (£)
Annual Carbon Dioxide Savings (kgCO₂)
Detached House
£4,300
£410
1,100
Semi-Detached House
£2,700
£240
650
Mid-Terrace House
£1,500
£140
380
Detached Bungalow
£2,000
£180
490
Mid-Floor Flat
£1,100
£110
310
Retrofitting Cavity Wall Insulation
Retrofitting insulation in existing walls presents its own set of challenges and considerations.
- Initial Assessment: It’s essential to assess the condition of the cavity and the suitability of the wall for insulation.
- Injection Process: Injected insulation must be evenly distributed to fill the cavity completely, avoiding any voids or gaps.
Addressing and Preventing Thermal Bridges
Thermal bridges are a significant concern in cavity wall insulation, as they can lead to up to 30% of heat loss in a well-insulated house.
Cost and Long-Term Savings
The cost of installing cavity wall insulation can vary, but it’s an investment that pays off in the long run.
- Estimated Costs: Retrofitting costs range from £1000 to £2500, depending on the house type.
- Long-Term Savings: Though the initial investment may seem substantial, the reduction in energy bills over time makes it a cost-effective decision.
Maintenance and Weatherproofing Considerations
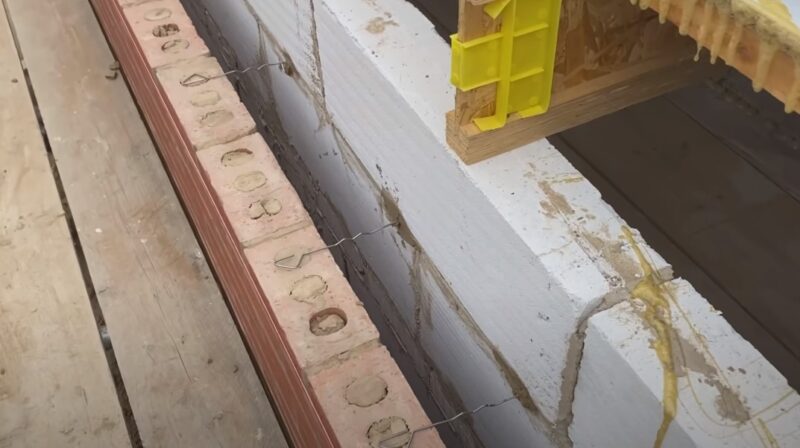

Proper maintenance and weatherproofing are critical to the long-term performance of cavity wall insulation. This aspect of insulation is often overlooked, yet it plays a significant role in preserving the integrity and effectiveness of the insulation material.
Weatherproofing
- Top of the Wall: Special attention should be given to weatherproofing the top of the wall. This prevents moisture ingress, which can compromise the insulation’s performance.
- Sealing Gaps: Ensuring that all gaps and cracks are sealed is crucial to prevent water and air leakage.
Regular Maintenance
- Inspections: Periodic inspections can help identify potential issues like moisture buildup or pest infestation, which can affect the insulation.
- Repairs: Timely repairs and replacements are necessary to maintain the insulation’s efficiency.
Special Considerations for Renovations

When it comes to renovations, installing cavity wall insulation requires a tailored approach. This is particularly true for older buildings, which may not have been designed with modern insulation standards in mind.
Existing Insulation
Assess the condition and type of any existing insulation. This will determine whether additional insulation is needed or if existing materials need replacement.
Cavity Presence
The decision to install internal wall insulation largely depends on whether there’s a cavity and its condition.
Compliance with Building Regulations

In new builds, compliance with Building Regulations is non-negotiable. These regulations are in place to ensure that the construction meets minimum standards for health, safety, and energy efficiency.
- Regulatory Standards: The installation must meet the current U-value requirement of 0.18W/m².
- Certification: Upon completion, it’s often necessary to have the insulation inspected and certified to comply with local building codes.
Environmental Considerations
Cavity wall insulation is not only about improving the thermal comfort of a building but also about reducing its environmental impact.
- Energy Conservation: By reducing the need for heating and cooling, insulation helps conserve energy.
- Sustainable Materials: Choosing eco-friendly materials can further enhance the building’s environmental performance.
Does Cavity Wall Insulation Cause Damp?
Is your Cavity Wall Insulation causing damp or mold problems within your home, then it may be time to get it replaced with a modern, long lasting alternative from Insul Xtract. https://t.co/7cPmI6D9X2 #CavityWallInsulation #Insulation #InsulationRemoval
— Trusted Local (@trustedlocaluk) December 21, 2024
There’s a common belief, even among some building professionals, that wall cavities should never be filled because insulating them will inevitably cause damp bridging. However, this is a misconception.
In the UK, approximately 4 million homes have had cavity wall insulation retrofitted. Instances where insulation has directly caused damp bridging are extremely rare. When water penetration does occur, it is almost always due to construction defects in the property rather than the insulation itself or its installation.
Issues like cracks or pre-existing damp problems are usually easy for a qualified assessor to identify and resolve. By addressing these defects beforehand, walls can be safely insulated without causing dampness problems. This highlights the importance of conducting a thorough assessment prior to installation.
Guaranteed for 25 Years
Reputable installers are typically registered with the Cavity Insulation Guarantee Agency (CIGA). CIGA provides a 25-year guarantee, covering problems caused by faulty or inappropriate installation of cavity wall insulation. If you already have cavity wall insulation and suspect an issue, you can contact CIGA to confirm if your guarantee is still valid.
In cases where defects in materials or workmanship are identified, CIGA works to resolve complaints to ensure customer satisfaction. If your property was insulated by an installer covered under the guarantee, it will be registered with CIGA. This ensures you have support should any problems arise.
FAQ
Conclusion
Cavity wall insulation is a key element in creating an energy-efficient, comfortable, and environmentally friendly home. Whether you’re dealing with a new build, a renovation, or retrofitting an existing property, understanding the types of insulation, installation techniques, maintenance, and regulatory compliance is essential.
By investing in quality insulation and ensuring its proper installation and upkeep, homeowners and builders can enjoy the benefits of a well-insulated property for years to come. Remember, the effectiveness of insulation lies not just in its installation but also in its ongoing maintenance and suitability to the specific needs of the building and its occupants.









